In today’s fast-changing financial markets, understanding volatility has become more important than ever before.
Events such as war, natural disasters, tariffs, earnings results and geopolitical tensions can send markets tumbling or surging within hours.
However, times of greater volatility can be a boon to the experienced trader, as larger price swings can provide potentially better trade entries and greater profits.
Among the various indicators available, the VIX - often referred to as Wall Street’s “fear gauge" - is one of the most popular measures of market uncertainty.
This article explains what the VIX is, how it’s calculated, why it matters, and how traders can use it to navigate turbulent markets.

What is the VIX?
The VIX, or CBOE Volatility Index, is designed to measure market expectations of near-term volatility conveyed by S&P 500 index options. In simple terms, the VIX is a snapshot of investor sentiment - it reflects the level of fear or complacency in the market.
When the VIX is high, investors expect larger price swings in the S&P 500; when it’s low, market participants are generally more confident and expect calmer conditions.
According to the CBOE’s official product page, the VIX is based on real-time option prices and serves as a benchmark for volatility in the U.S. equity markets.
The VIX is calculated using a wide range of S&P 500 option prices, providing a weighted average that represents the market’s forecast of volatility over the next 30 days.
This characteristic has earned the VIX its popular nickname - the “fear gauge” - since sudden spikes in the VIX typically accompany periods of market stress and uncertainty.
How is the VIX Calculated?
The process behind the VIX’s calculation is both sophisticated and illuminating. Rather than measuring past price changes, the VIX is derived from the implied volatility of a wide range of put and call options on the S&P 500.
These options reflect investor sentiment about the pace and magnitude of potential market movements. When traders buy or sell options, the prices they accept and the strike prices they choose indicate their expectations of future volatility.
By aggregating these premiums across a wide range of strike prices, the VIX provides a forward-looking view of market sentiment.
This method distinguishes the VIX from other volatility measures that rely solely on historical data. The fact that the VIX is based on option prices means it captures real-time changes in investor psychology and expectations.
As a result, it can quickly reflect emerging risks or a shift toward market optimism.
The ‘Fear Gauge’
Why is the VIX so closely associated with fear? The answer lies in its historical behaviour. During times of economic distress - such as financial crises or geopolitical shocks - investors tend to buy more options to hedge against potential losses, driving up option premiums and, consequently, the VIX.
Conversely, when the market is calm, fewer investors feel the need for such protection, and the VIX tends to remain low.
As noted in S&P Global's A Practitioner's Guide to Reading VIX, "If market participants are rationally processing what might already be deduced about future volatility - from upcoming earnings, central bank announcements, political events, and so on, as well as from the expected frequency of unanticipated market moving events - then VIX might be said to provide a crowd-sourced estimate of the degree to which the market is uncertain about the future."
For many market participants, the VIX is a barometer of investor emotion. A sudden and sharp increase in the VIX often signals a move from complacency to caution, alerting traders that a period of turbulence may be imminent.
This dynamic has made the VIX a critical tool not only for gauging market sentiment but also for formulating trading strategies.
Historical Perspective: Lessons from the Past
Examining the historical performance of the VIX can provide valuable context for today’s market environment. Macrotrends’ historical chart of the VIX shows that, over the long term, the index has experienced dramatic swings during periods of financial stress.
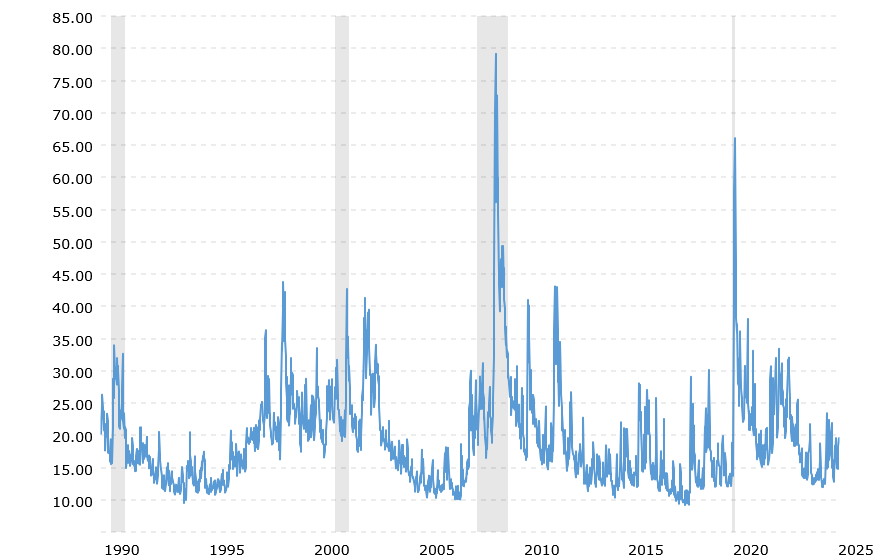
For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the VIX spiked to levels far above its typical range, reflecting the extreme uncertainty of that period.
In 2025, while the VIX has been on an upward trajectory in recent months, current levels remain moderate compared to past crises. This historical perspective suggests that, although the market is more volatile than during calmer periods, there is still room for further movement should conditions deteriorate.
Australian Perspective: The S&P/ASX 200 VIX Index
For Australian investors, volatility is measured not only by the U.S.-based VIX but also by the S&P/ASX 200 VIX index, often referred to as the A-VIX.
The S&P/ASX 200 VIX provides a real-time indicator of market sentiment in the Australian equity market by tracking the implied volatility of options on the S&P/ASX 200 index.
The A-VIX operates similarly to its U.S. counterpart: a high A-VIX value indicates that market participants expect large swings in the S&P/ASX 200, signalling uncertainty and potential bearish sentiment, while a low value suggests a more stable market outlook.
This index is particularly useful for Australian investors who wish to gauge local market conditions and align their strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
The VIX remains a vital indicator in a trader’s arsenal, serving as a real-time gauge of market fear and uncertainty. With its foundation in the prices of S&P 500 options, the VIX offers a forward-looking perspective that investors can use to identify periods of panic and caution.
While historical data and current market signals suggest that there is potential for further spikes in volatility, particularly in light of economic and political pressures, traders who remain vigilant and employ robust risk management strategies will be better positioned to capitalise on these moves.
In an environment where fear and opportunity often go hand in hand, the ability to decode the signals of the “fear gauge” can make the difference between significant losses and strategic gains.
As we move forward in a year marked by both promise and uncertainty, the VIX will undoubtedly continue to serve as a critical indicator of market sentiment.
For traders willing to look beyond mere price action and delve into the psychology of the markets, the VIX offers a window into the collective mindset of investors.
As the adage says, “In times of crisis, opportunity arises.” For traders focused on volatility, the unfolding market conditions of 2025 may indeed represent one of the most challenging - and potentially rewarding - periods in recent history.



